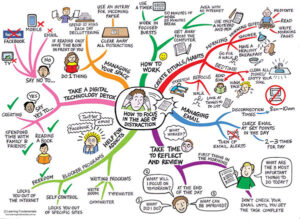
Choosing the Right SEO Company for Digital Marketing
In the vast landscape of the internet, getting noticed can be quite the challenge. Whether you’re a budding startup or an established business, harnessing the power of digital marketing is essential. And at the heart of effective digital marketing lies the selection of a proficient SEO (Search Engine Optimization) company. But where do you begin, especially if you’re new to this? We’re here to guide you through the process in simple terms.
1. Understand Your Goals:
First and foremost, know what you want to achieve with digital marketing. Are you looking to boost website traffic, increase sales, or enhance your online presence? Your goals will determine the type of SEO services you need.
2. Ask for Recommendations:
Turn to your network, colleagues, or fellow business owners for recommendations. Hearing about real experiences with SEO companies can be incredibly valuable.
3. Do Your Homework:
Research potential SEO companies online. Look at their websites, read client reviews, and assess their portfolio. Get a sense of their expertise and the industries they’ve worked in.
4. Seek Transparency:
When reaching out to SEO companies, make sure they are transparent about their processes. Ask them about their strategies, the tools they use, and how they plan to measure success.
5. Assess Your Budget:
Digital marketing can vary in cost. Be clear about your budget, and see if the SEO company can work within those constraints. Remember, SEO is an investment in your business’s online future.
6. Look for Experience:
Experience matters in the SEO world. An experienced company is more likely to have a deep understanding of search engine algorithms and industry trends.
7. Get a Customized Plan:
A one-size-fits-all approach rarely works in digital marketing. A good SEO company should offer you a customized plan tailored to your specific needs and goals.
8. Ask About Reporting:
Inquire about how the company will provide you with progress reports. Regular updates and data insights are crucial for assessing the effectiveness of the SEO strategy.
9. In-House Team vs. Outsourcing:
Understand whether the SEO company has an in-house team or if they outsource their work. In-house teams often provide better control and communication.
10. Assess Their Communication:
Effective communication is key. Ensure the SEO company is responsive and that you can reach them when you have questions or concerns.
11. Avoid Promises of Instant Results:
Be cautious of companies that promise instant or guaranteed results. SEO takes time to yield tangible outcomes, and ethical SEO companies will set realistic expectations.
12. Trust Your Instincts:
Finally, trust your gut feeling. Choose a company that you feel comfortable and confident working with.
Selecting the right SEO company is like finding a business partner for your online success. Take your time, do your research, and choose a company that aligns with your goals and values. Your digital marketing journey starts with this essential step.
- Published in Digital Marketing, Networking
Web 1.0 Pioneering the Internet Frontier-Era 1
Web 1.0 stands as the genesis of the modern internet, laying the foundation for the vast digital landscape we navigate today. During this era, the internet emerged as a groundbreaking communication tool, transforming the world’s accessibility to information. In this article, we will delve into the inception of Web 1.0, its SEO-friendly characteristics, easily comprehensible language, and explore some key pioneers who played a significant role in its development.
Web 1.0 was a transformative era in the history of the internet, setting the stage for the digital revolution that followed. The simplicity of language and user-friendly design principles of Web 1.0 content unwittingly contributed to the foundation of SEO practices we employ today. The brilliance of the scientists and pioneers involved paved the way for a vast, interconnected world where information is readily accessible to billions of users worldwide. As we continue to evolve and innovate in the digital landscape, we owe a debt of gratitude to these visionaries who blazed the trail and forever changed the way we interact with information.
The Birth of Web 1.0
Web 1.0, also known as the “Static Web,” introduced static web pages and limited user interaction. It marked the beginning of the internet era, where content creators published information on websites, and users consumed this information passively. During this phase, the World Wide Web took its first steps toward becoming a global platform for sharing knowledge and connecting people.
Language Accessibility of Web 1.0
In the early days of Web 1.0, content creators recognized the importance of communicating complex ideas in simple terms. They aimed to make information accessible to a broader audience, and as a result, web content was presented in basic, user-friendly language. This approach directly reached the subconscious mind of the readers, facilitating a greater understanding of the digital landscape.
Key Scientists and Pioneers of Web 1.0
Web 1.0 owes its existence to several brilliant minds who played significant roles in its development. Some notable scientists and pioneers include:
- Sir Tim Berners-Lee: Credited as the inventor of the World Wide Web, Sir Tim Berners-Lee developed the first web browser and laid the foundations for linking web pages through hyperlinks.
- Marc Andreessen: Co-author of the Mosaic web browser, Andreessen played a vital role in popularizing the graphical user interface (GUI) of Web 1.0, making the internet more visually appealing and user-friendly.
- Larry Page and Sergey Brin: Though they gained prominence later, Page and Brin were early contributors to the development of Web 1.0. Their creation of Google revolutionized web search and information retrieval, making content discovery faster and more efficient.
- Vint Cerf and Bob Kahn: Known as the “Fathers of the Internet,” Cerf and Kahn co-developed the TCP/IP protocol suite, the fundamental communication protocol that enabled the internet to function globally.
- Published in Technology
Web 2.0 Embracing Interactivity and Collaboration in the Digital Age- Era 2
The advent of Web 2.0 marked a significant turning point in the evolution of the internet. With its dynamic and interactive nature, Web 2.0 revolutionized the way people interacted online, fostering a sense of community and collaboration. In this article, we will delve into the inception of Web 2.0, its SEO-friendly characteristics, easily comprehensible language, and explore some key pioneers who played a significant role in its development.
The Emergence of Web 2.0
Web 2.0 emerged in the early 2000s, signifying a shift from the static, one-way flow of information of Web 1.0 to a more participatory and user-centric web experience. This era emphasized user-generated content, social networking, and web applications that facilitated collaboration and interaction among internet users.
Language Accessibility
Web 2.0 recognized the importance of user-friendly language to create engaging and interactive experiences. Content creators embraced easily comprehensible language, allowing users to actively participate and contribute to online discussions, forums, and social media platforms. This user-centric approach fostered a strong connection between content creators and their audiences, making the internet a more inclusive and accessible space.
The transition from Web 1.0 to Web 2.0 marked a significant shift in the nature and functionality of the internet. Here’s how this technology changed the web from Web 1.0 to Web 2.0:
- User Participation and Interactivity: In Web 1.0, the internet primarily consisted of static web pages with limited user interaction. Content was primarily published by website owners, and users were passive consumers of information. However, with the rise of Web 2.0, user participation and interactivity became central to the web experience. Web 2.0 platforms encouraged user-generated content, social networking, and collaboration, allowing users to actively participate by creating, sharing, and interacting with content.
- Social Media and Networking: Web 2.0 saw the emergence of social media platforms that transformed how people connected and communicated online. Platforms like Facebook, Twitter, and LinkedIn allowed users to create profiles, connect with friends and colleagues, and share updates in real-time. Social media became an integral part of everyday life, fostering a sense of online community and enabling users to engage in discussions and share experiences.
- User-Centric Content Creation: In Web 1.0, content creation was primarily the domain of website owners and developers. Web 2.0 platforms, on the other hand, empowered users to become content creators. Blogs, forums, and wikis allowed users to publish their thoughts, ideas, and knowledge, giving rise to user-generated content. Wikipedia, as a prime example, demonstrated how collective intelligence could lead to a vast repository of knowledge, created and maintained by volunteers worldwide.
- Collaboration and Collective Intelligence: Web 2.0 emphasized collaboration and the power of collective intelligence. Online tools and platforms enabled users to collaborate on projects, share resources, and work together irrespective of geographical boundaries. This led to the growth of collaborative platforms, cloud-based applications, and online document sharing tools that facilitated remote teamwork and information exchange.
- Rich Media and Multimedia: Web 2.0 witnessed a surge in the use of rich media and multimedia content. With the advancement of technology, websites started incorporating videos, images, and interactive elements to enhance user engagement. Platforms like YouTube became popular, allowing users to share and consume videos on a global scale, changing how people accessed and interacted with media content.
- Personalization and Customization: Web 2.0 platforms introduced personalization features, tailoring content and recommendations based on users’ preferences and behaviors. This created a more personalized web experience, with content and advertisements targeted to individual users, making the internet feel more relevant and engaging.
Overall, the transition from Web 1.0 to Web 2.0 represented a shift from a passive, one-way flow of information to an interactive, participatory, and user-centric web experience. The internet evolved into a dynamic and collaborative space, enabling people worldwide to connect, share, and collaborate on an unprecedented scale. This transformation laid the groundwork for further advancements and paved the way for the dynamic and immersive digital landscape we experience today.
Key Pioneers and Innovators of web 2.0
Several visionaries and pioneers shaped the landscape of Web 2.0, transforming the internet into a dynamic and collaborative platform. Some of the key pioneers include:
- Tim O’Reilly: Coined the term “Web 2.0” and played a crucial role in popularizing the concept and principles behind it. O’Reilly emphasized the importance of user-generated content and the power of collective intelligence.
- Mark Zuckerberg: Co-founded Facebook, a social networking platform that revolutionized online communication and connectivity. Facebook allowed users to share, connect, and interact in real-time, making it a cornerstone of Web 2.0.
- Jimmy Wales and Larry Sanger: Co-founded Wikipedia, an online encyclopedia that relied on collaborative content creation by users worldwide. Wikipedia demonstrated the potential of collective knowledge sharing and collaborative information gathering.
- Jack Dorsey, Biz Stone, and Evan Williams: Co-founded Twitter, a microblogging platform that encouraged real-time sharing of short messages. Twitter became a powerful tool for information dissemination and online discussions.
- Published in Technology